Overview of hernias
What is a hernia?
A hernia is the protrusion of tissue through a weak spot in the surrounding wall of the cavity that normally contains it. Because of this localized 'hole' of the wall, an organ or a part of an organ squeezes into another region of the body. Quite often, this condition results into a visible bulge against the skin.
Depending on where this protrusion takes place there are different kinds of hernias, each requiring a specific management and treatment. By far, the most common hernias develop through various abdominal wall defects.
Common types of abdominal wall hernias
- Hernias of the groin
- Inguinal Hernia (inner groin)
- Femoral Hernia (outer groin)
- Hernias of the midline
- Umbilical Hernia (navel - belly button)
- Epigastric Hernia (midline above the navel)
- Incisional Hernia (after surgical incision)
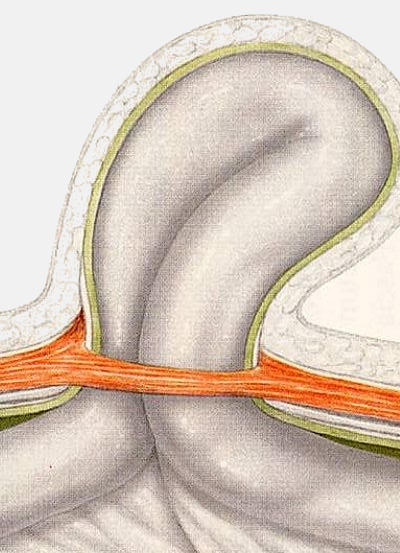
Hernia signs and symptoms
Asymptomatic hernia
Often localized swelling and often visible bulge at the hernia site
No pain or discomfort at most times. Sometimes aching sensation around the area of the hernia
Swelling often enlarges while standing and disappears while lying or manually
Watchful waiting possible
Surgery recommended
Symptomatic hernia
Localized swelling and visible bulge at the hernia site in most cases
Recurrent pain and discomfort, especially during physical effort, laughing, coughing etc.
Swelling often enlarges while standing and may disappear while lying or manually
Surgery strongly recommended
Incarcerated hernia
Painful swelling at the hernia site, very sensitive to local pressure
Frequently occurring pain attacks. Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting possible
Usually enlargement of previously known bulge. It does not disappear while lying or manually
Urgent surgery required
Strangulated hernia
Very painful swelling at the hernia site, extremely sensitive to pressure
Constant massive pain at the hernia site. Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting probable
Usually enlargement of previously known bulge. It does not disappear while lying or manually
Emergency surgery required
FAQ: I have been recently diagnosed with a inguinal hernia. I can see and feel the bulge myself but I don't have any discomfort at all. Is hernia repair surgery recommended at this time?
Surgery is recommended for abdominal wall hernias
Leaving an abdominal wall hernia without surgical treatment is not really an option, plenty of clinical studies in the last decades have proven that. Please consider:
No spontaneous healing
An abdominal wall hernia will not heal on its own. There is no way of fixing the 'hole' with some kind of exercise or medication. If the hernia defect is there, it can only enlarge over time making a future surgical repair even more complicated.
Pain and discomfort
Most patients with a hernia will develop discomfort and pain over time, even if the hernia is not causing any symptoms in the beginning. These symptoms can noticeably affect the patient's quality of life and ability to work.
Hernia belts not effective
Non-surgical treatments, such as wearing a belt or corset, will definitely not solve the problem. In fact they can cause additional issues and they are considered to be old-fashioned and in some cases even dangerous.
Strangulation possible
A potentially life-threatening strangulation of the hernia contents can occur any time, if the hernia is left untreated.
FAQ: I have a bulge in my groin, which sometimes gets very painful, especially after exercise. Some time later the symptoms decline. Is that a dangerous condition?
Hernia: a potentially dangerous condition
A hernia of the groin or the abdominal wall is certainly not only an aesthetic issue, because of a resulting visible bulge. The protrusion of tissue into another area of the body is often combined with discomfort and pain, which worsens with increasing intraabdominal pressure (cough, laugh, exercise, etc.) or even automatically with bowel movements.
The main problem, however, is that the tissue inside a hernia can anytime be strangulated and its blood supply can be interrupted. This condition can rapidly lead to permanent damage to intraabdominal organs and even threaten the patient's life.
"hernia repair surgery is highly recommended as soon as the first symptoms appear"
Methods of hernia repair
The abdominal wall hernia is a very common condition, affecting approximately 10% of the population. Hernia repair is the most frequently performed surgery in the world, as millions of hernia operations take place each year. Nowadays, there are several different approaches to hernia repair, some much more successful than others.
Learn more about surgical procedures in hernia repair surgery

